Improvement of Care & Outcome
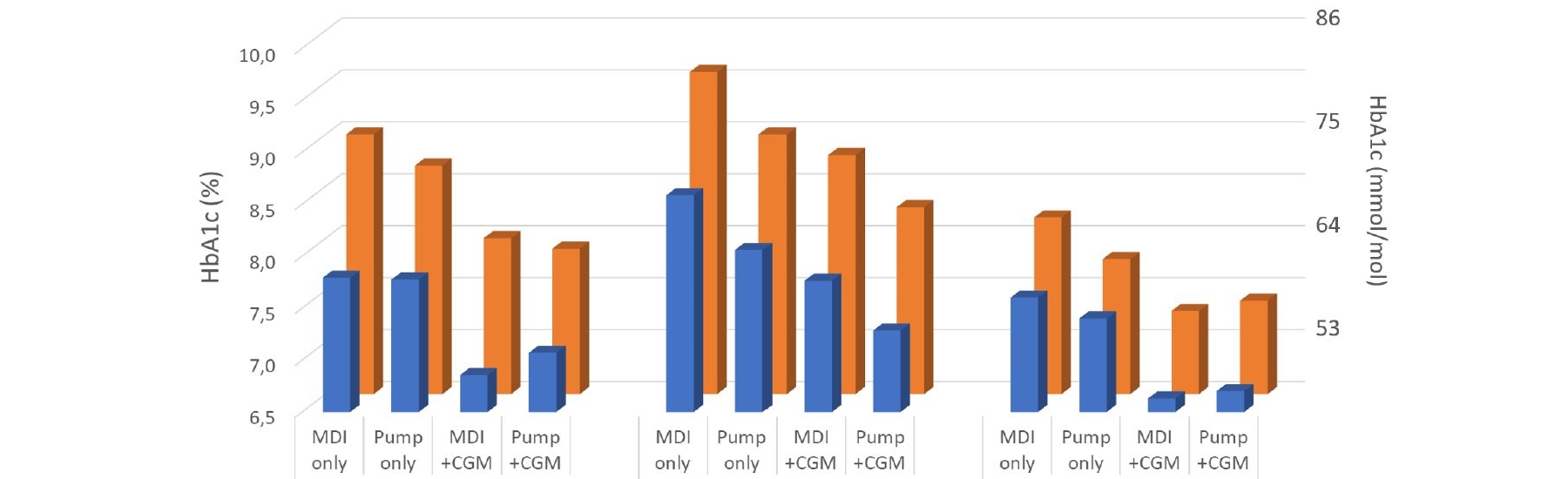
Although diabetes technology (e.g. insulin-pumps including CGM and FGM) can improve glycemic control in controlled trials, better outcomes through increased use were not seen in real-world data from T1D Exchange (DTT 2019). Diabeter delivers standardized, value-based, comprehensive type 1 diabetes care. To try to explain outcome differences between Diabeter and T1D Exchange, technology use and eHealth activities were evaluated.
Cross-sectional data from 2018 on treatment modality (MDI/pump), uploads, glucose monitoring methods (SMBG/FGM/CGM) and A1C (last value of year) were extracted from Vcare, Diabeter’s custom-build electronic disease management system. To establish the overall improvement in care/outcome between 2017 and 2018 an in-house developed measure, the individual net improvement score (NIS), was used.
Key Findings: